You sell "dimmable" LED filament bulbs, but your customers complain about annoying flickering, buzzing, or bulbs that just won't dim properly. These performance issues lead to costly returns, negative reviews, and ultimately damage your brand's reputation for quality.
True flicker-free dimming requires perfectly matching the bulb's internal driver with the right dimmer switch (usually a modern trailing-edge or universal dimmer). The primary cause of poor performance is an incompatibility between a modern LED bulb and an older, leading-edge dimmer designed for incandescent loads.

I remember a major project we supplied for a hotel chain in the United States a few years back. The product manager, let's call him Jacky, meticulously chose our high-CRI ST64 filament bulbs for 300 guest rooms. The initial samples performed flawlessly. But two weeks after the full installation, I got a frantic call. In nearly half the rooms, the bulbs were flickering uncontrollably at mid-level, and a faint but maddening buzz was audible when the rooms were quiet. The hotel was threatening to rip out the entire installation. My first question wasn't about the bulbs, but about the dimmers. It turned out the contractor, to save costs, had used older, cheaper leading-edge dimmers they had in stock. We overnighted ten of our recommended trailing-edge dimmers. They swapped them out in the problem rooms, and the issues vanished completely. Jacky had to spend extra to replace all 300 dimmers, a costly lesson in the critical partnership between a bulb and its switch. That day taught me that selling a "dimmable bulb" is only half the job; ensuring our customers understand compatibility is the key to success.
What's the Real Cause of LED Flickering and Buzzing?
Your customer has installed your beautiful new filament bulbs, but they're seeing an irritating flicker or hearing a constant buzz. Is the bulb defective, or is there a more complex technical issue at play that could affect your entire product line?
Flicker and buzz are symptoms of an electrical conflict between the LED bulb's internal driver and the dimmer switch. This "incompatibility" arises because older dimmers cut the power wave in a way that the bulb's sensitive electronics cannot smoothly interpret.
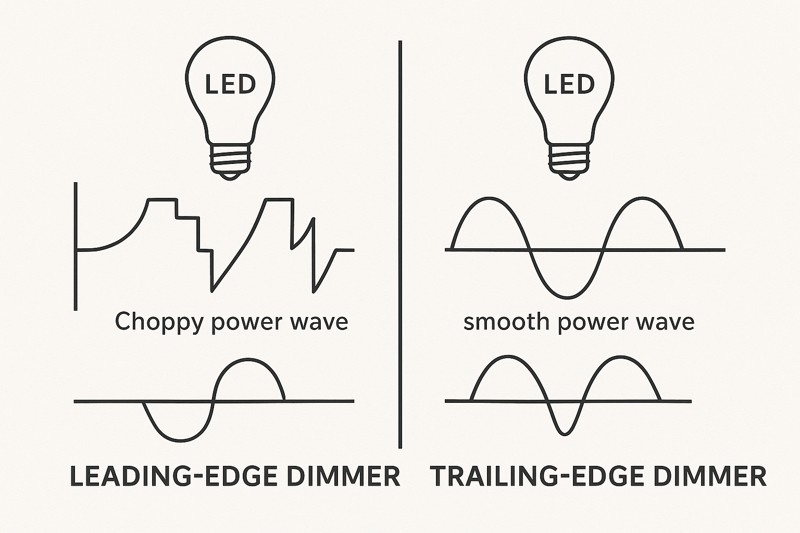
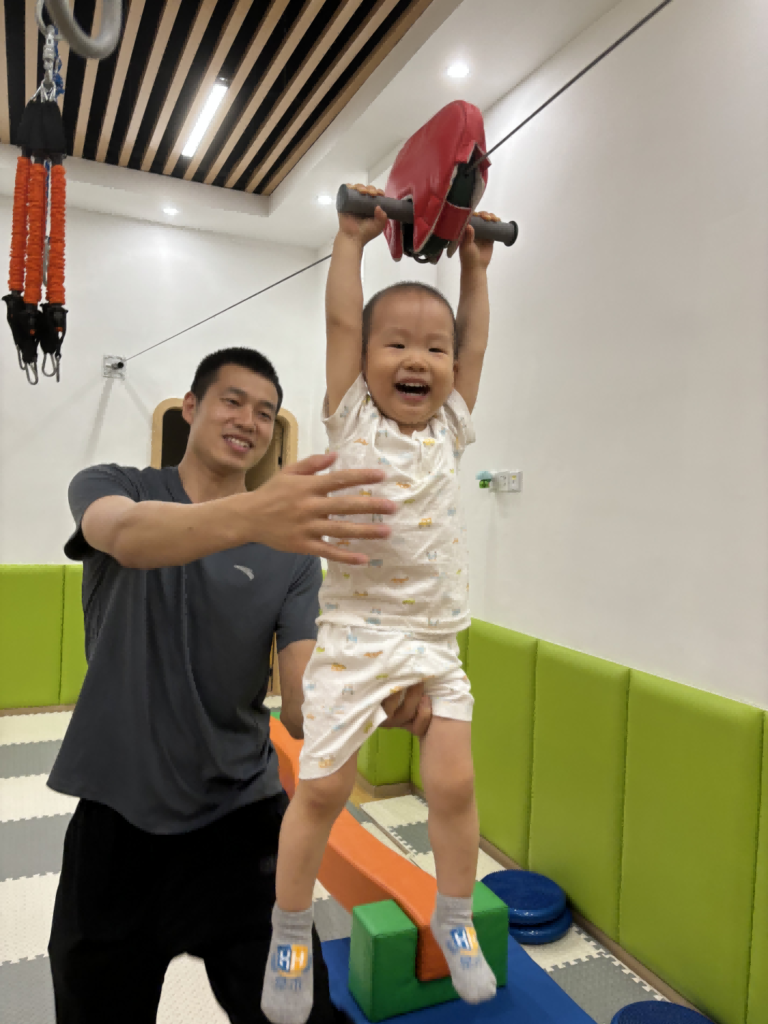
To understand dimming, you have to look at how dimmers work. A traditional incandescent bulb was simple: you reduced the power, and the filament glowed less brightly. The dimmers for these, called Leading-Edge (TRIAC) dimmers, worked by cutting off the front part of the AC power wave. This was a crude but effective method for a simple resistive load like a glowing wire. An LED filament bulb, however, is a sophisticated electronic device. It contains a "driver" – a miniature computer that converts high-voltage AC power into the low-voltage DC power the LEDs need. This driver needs a clean, stable power signal. When a leading-edge dimmer chops the power wave, the driver struggles to make sense of the erratic signal. This can cause the LEDs to turn on and off rapidly (flicker) or cause components in the driver to vibrate (buzz). To solve this, a newer type of dimmer, the Trailing-Edge (ELV) dimmer, was invented. It cuts the back half of the power wave, which is a much smoother and cleaner signal for the LED driver to process. This results in smooth, silent, and flicker-free performance. As a manufacturer, we design our Hongyu Bulb drivers to be compatible with the widest range of dimmers possible, but performance will always be superior with a modern, high-quality trailing-edge dimmer.
The Technical Showdown: Leading-Edge vs. Trailing-Edge
Educating your customers on this difference can prevent 90% of dimming complaints.
| Dimmer Type | Technology | Designed For | Performance with LEDs |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leading-Edge (TRIAC)1 | Old, simple. Chops the start of the AC wave. | Incandescent & Halogen Bulbs | Poor. High risk of flicker, buzz, and limited dimming range. |
| Trailing-Edge (ELV)2 | Modern, complex. Cuts the end of the AC wave. | LEDs, Electronic Low Voltage Transformers | Excellent. Smooth, silent, wide dimming range. |
| Universal (C-L Type) | Adaptive technology. | Both incandescent and LED loads. | Good to Excellent. Tries to auto-detect and provide the best performance. |
Your key takeaway for customers: If you are upgrading to LED lighting, you must consider upgrading your dimmer switches to a modern Trailing-Edge or Universal model for guaranteed performance. It's not an upsell; it's a necessary part of the system.
How Low Can You Go? Understanding Dimming Range and Drop-Out
A customer wants to dim their restaurant lights for a cozy, candle-lit mood, but the bulbs simply turn off when the dimmer is below 20%. Has the bulb failed, or is this a normal limitation of the technology?
The dimming range, or how low a bulb can dim, is determined by the quality of its internal driver. Cheaper drivers require a higher minimum power level to operate, causing them to "drop-out" or turn off at 10-20% brightness, while premium drivers can dim smoothly down to 1-5%.
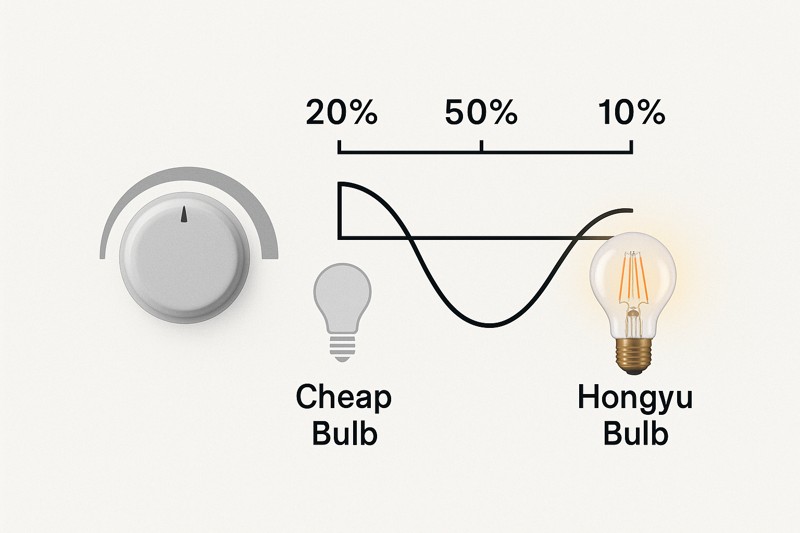
The ability to dim deeply and smoothly is a hallmark of a high-quality LED bulb. The internal driver needs a certain amount of power just to stay "on" and function. In a low-quality bulb, the driver components are cheaper and less efficient. When the dimmer reduces the power to a very low level (e.g., below 10%), the driver can't sustain itself and simply shuts off—this is called "drop-out." Conversely, a premium driver, like the ones we engineer at Hongyu Bulb, uses more sophisticated components that are designed for low-power operation. This allows our bulbs to maintain a stable, flicker-free light even when dimmed down to 5%, 3%, or even 1% of their total brightness, mimicking the deep dimming capabilities of an incandescent bulb. Another related issue is "pop-on." This happens when you have the dimmer at a very low setting and turn the power on; a low-quality bulb won't light up until you turn the dimmer up to a certain threshold (e.g., 15%) and then turn it back down. A high-quality bulb will turn on smoothly even at the lowest dimmer setting.
The Impact of Dimming Range on Application
The required dimming range3 is not the same for every situation.
| Application | Required Dimming Range | Why it Matters | Recommended Bulb Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Home Office / Kitchen | 30% - 100% | Task lighting adjustments; mood is secondary. | Standard Quality Driver |
| Living Room / Bedroom | 10% - 100% | Needs to transition from bright to relaxed. | High-Quality Driver |
| Restaurant / Bar / Theatre | 1% - 100% | Atmosphere is critical. Needs to dim to a near-candlelight level. | Premium-Grade "Deep Dimming" Driver |
When a customer like a restaurant owner asks for dimmable bulbs, their actual need is for deep dimming. By offering bulbs with certified low-level dimming performance (e.g., "dims to 1%"), you are providing a professional solution that commands a higher price and builds trust.
How Do You Solve the "Pop-On" and Inrush Current Problem in Large Installations?
An electrical contractor is installing 50 of your LED bulbs on a single circuit in a large ballroom. When they flip the switch, the circuit breaker trips instantly. Is your product defective and drawing too much power?
This is caused by "inrush current," a momentary power surge that occurs as all the bulb drivers' capacitors charge at once. While normal for a few bulbs, it can trip breakers in large installations. The solution is a high-quality driver with "soft-start" circuitry.
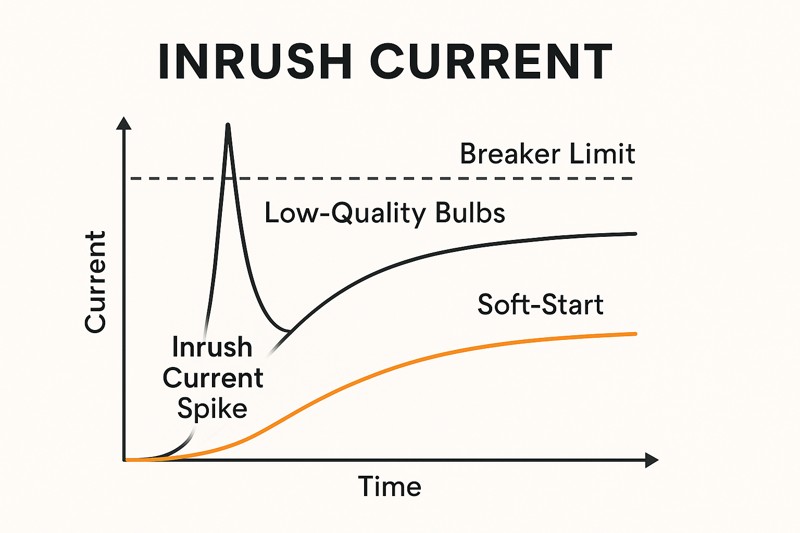
This is a highly technical problem that can derail large commercial projects. When you turn on an LED bulb, its driver has capacitors that need to charge instantly. This creates a very brief but very large spike of current, many times the bulb's normal operating current. For one or two bulbs, this is harmless. But when you have 30, 50, or 100 bulbs on one circuit all demanding that power at the exact same microsecond, the combined inrush current can exceed the breaker's limit (e.g., 15 Amps), causing it to trip for safety. The contractor might assume the bulbs are faulty or that the total wattage is too high, but the real culprit is that instantaneous power surge. As a responsible manufacturer catering to professional clients, we have engineered "soft-start" technology into our premium drivers. A soft-start circuit is like a traffic manager for electricity; it gently ramps up the power to the driver over a fraction of a second instead of demanding it all at once. This effectively flattens that massive inrush current spike, allowing many bulbs to be used on a single circuit without tripping the breaker.
Managing Load for Professional Installations
This is a critical selling point for electricians and commercial lighting specifiers.
| Problem | Low-Quality Driver | High-Quality Soft-Start Driver | Benefit for the Installer |
|---|---|---|---|
| Inrush Current | Large, instantaneous spike. | Controlled, gentle ramp-up.4 | Prevents tripped breakers, saving time and money. |
| Bulb "Pop-On" | Bulbs flash on at full brightness before dimming. | Smooth, gradual turn-on.5 | A more elegant and high-end lighting experience. |
| Max Bulbs per Circuit | Limited by inrush current, not just wattage. | Can install more bulbs on one circuit. | Simplifies wiring and reduces the number of circuits needed. |
By offering a product with a soft-start driver, you are directly solving a major pain point for commercial installers. It proves that you understand the challenges of real-world installations and have engineered a robust, professional-grade solution.
Can Dimming Recreate the Warmth of a Traditional Bulb?
Your customer installed your 2700K dimmable bulbs, but they complain that when dimmed for a cozy evening, the light just looks grey and dull. The mood is ruined, and they blame your product's quality for not feeling "warm" like their old bulbs.
Standard LEDs maintain their color temperature when dimmed, becoming a less-bright version of the same color. For a true incandescent feel, you need a specialty product with "Warm Dim" or "Dim-to-Warm" technology, which actively lowers the Kelvin temperature as the bulb dims.

This is a premium feature that solves a major dissatisfaction point for discerning customers. For a century, we've been conditioned by incandescent and halogen bulbs, which naturally become warmer in color as they dim. A fully bright incandescent is about 2700K, but when dimmed to 10%, its glow becomes a very warm, candle-like 2000-2200K. Standard LEDs do not do this. A standard 2700K LED, when dimmed to 10%, is still 2700K—it just becomes a dim, somewhat uninspiring greyish-yellow light. This fails to create the intimate, cozy atmosphere people expect from dimmed lighting. As a premium manufacturer, Hongyu Bulb has invested in Warm Dim technology. These advanced bulbs have multiple types of LED chips (e.g., both 2700K and 2200K chips) on their circuit boards and a smart driver. As you lower the power from the dimmer switch, the driver intelligently shifts the power from the 2700K LEDs to the 2200K LEDs, smoothly transitioning the color temperature from a functional warm white to a decorative amber glow.
Selling the "Perfect Mood" with Warm Dim
This is not a standard feature; it is a high-value upgrade you can sell for a significant premium.
| Feature | Standard Dimmable LED | Warm Dim LED6 | Customer Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Color at 100% | 2700K (Warm White) | 2700K (Warm White) | Bright, functional light for tasks. |
| Color at 10% | 2700K (Looks grey/dull) | ~2200K (Cozy amber glow) | Authentic incandescent dimming experience. |
| Best Application | General purpose areas. | Living rooms, bedrooms, dining rooms, high-end bars. | The ability to transform a room's atmosphere. |
By adding Warm Dim bulbs to your portfolio, you are offering a true problem-solving product. It positions you as a technology leader and gives your buyers a high-margin product to offer their most valuable customers who want the best possible lighting experience.
Conclusion
Guarantee success by matching quality bulbs with compatible trailing-edge dimmers. Offer drivers with deep dimming ranges and soft-start for professional jobs, and provide premium Warm Dim options for the ultimate atmospheric control.
Learn how Leading-Edge dimmers can negatively impact LED performance, helping you make informed choices for your lighting needs. ↩
Explore the advantages of Trailing-Edge dimmers to ensure optimal performance and eliminate flickering with your LED lights. ↩
Understanding dimming range is crucial for selecting the right lighting for various environments, enhancing both functionality and ambiance. ↩
Explore how a controlled ramp-up can enhance installation efficiency and reduce electrical issues. ↩
Learn about the advantages of gradual turn-on for improving lighting quality and user experience. ↩
Explore the advantages of Warm Dim LED lighting to enhance your understanding of its unique benefits and applications. ↩







